一起学Java(11)-[日志篇]教你分析SLF4J源码,掌握Logger接口实现类加载原理
最近各种事情很忙,今天继续。在第十篇(一起学Java(10)-为项目引入Log框架(Log篇二-引入SLF4J接口层框架))中,我们为项目(https://github.com/lihongzheshuai/java-all-in-one)引入了SLF4J和Logback框架,按计划通过阅读源码研究下SLF4J的实现原理。
一、配置Gradle自动下载源码和Javadoc
为了便于的IDEA中自动绑定并阅读源码,首先配置Gradle的idea插件,在更新下载依赖的时候自动下载源码和Javadoc,修改build.gradle.kts文件,引入并配置idea插件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
plugins {
id("java")
id("idea")
}
allprojects {
group = "com.coderli"
version = "0.1"
}
subprojects {
apply(plugin = "java")
apply(plugin = "idea")
idea {
module {
isDownloadSources = true // 下载源码
isDownloadJavadoc = true // 下载 Javadoc
}
}
dependencies {
implementation("org.slf4j:slf4j-api:2.0.16")
implementation("ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:1.5.6")
}
repositories {
maven("https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public")
maven("https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/nexus/repository/maven-public/")
mavenCentral()
}
}
刷新项目后,依赖对应的源码即下载并帮定完成。点击进入第三方包的代码后,会直接显示源码而不是反编译的结果。可读性更强。
二、源码解读SLF4J如何寻找Log实现层框架
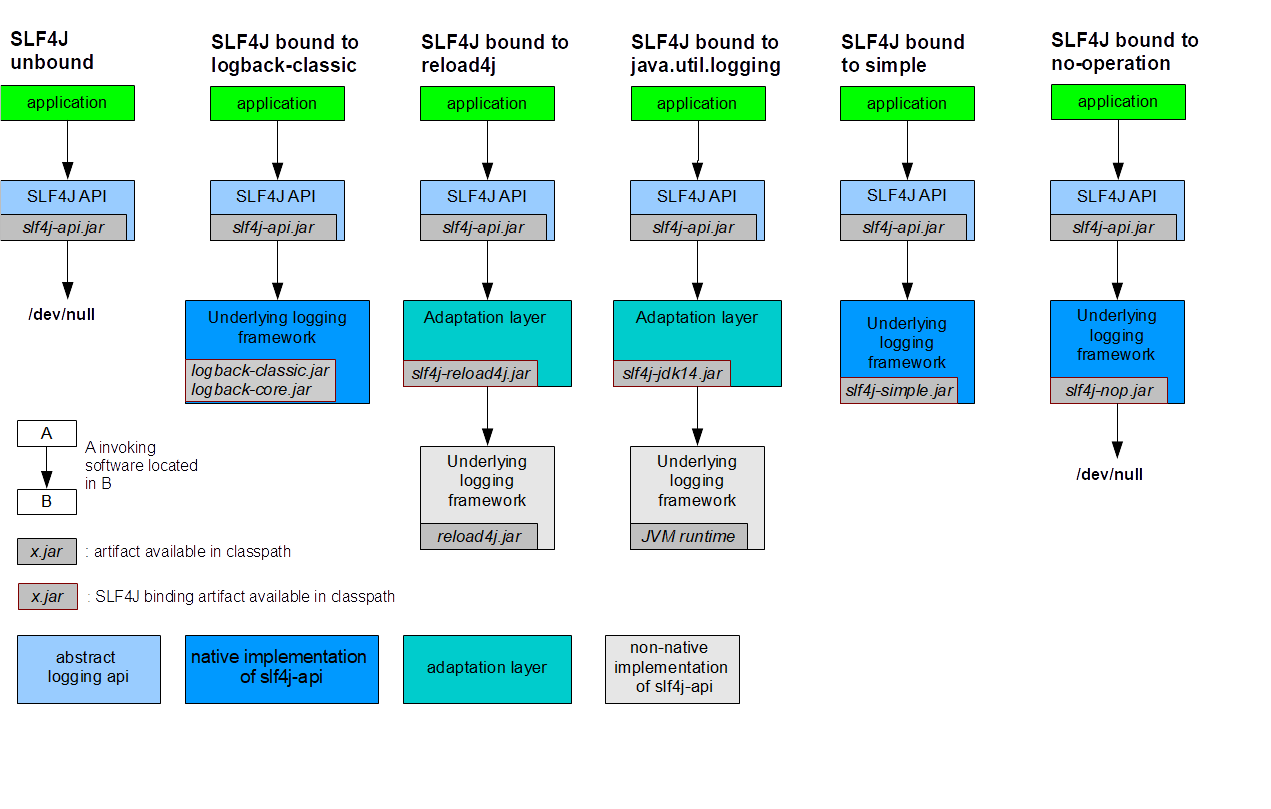
上文中(一起学Java(10)-为项目引入Log框架(Log篇二-引入SLF4J接口层框架)),在未引入Logback应用层框架的时候,打印日志时控制台输出:
1
2
3
SLF4J(W): No SLF4J providers were found.
SLF4J(W): Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J(W): See https://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#noProviders for further details.
以找到这个原因为研究目标,进行代码阅读。
Log应用层代码
SLF4J的使用方式代码是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
package com.coderli.one.log;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @author OneCoder
* @Blog https://www.coderli.com
*/
public class LogMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogMain.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}
即通过org.slf4j.LoggerFactory获取org.slf4j.Logger接口对应的实现类。
org.slf4j.LoggerFactory 实现代码
org.slf4j.LoggerFactory中依次调用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz) {
Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName());
if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH) {
Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass();
if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass)) {
Reporter.warn(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \"%s\"; computed name: \"%s\".", logger.getName(),
autoComputedCallingClass.getName()));
Reporter.warn("See " + LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL + " for an explanation");
}
}
return logger;
}
调用重载函数getLogger
1
2
3
4
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}
ILoggerFactory是SLF4J中的工程类接口,这里的逻辑是通过getILoggerFactory函数去获取Log框架实现层提供的LoggerFactory工厂类实例,获取到工厂类,既然就可以通过工厂类获取到Log实例。
getILoggerFactory实现逻辑为:
1
2
3
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
return getProvider().getLoggerFactory();
}
即先获取Factory的提供者Provider,通过Provider获取到LoggerFactory的实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
static SLF4JServiceProvider getProvider() {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
synchronized (LoggerFactory.class) {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION;
performInitialization();
}
}
}
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) {
case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION:
return PROVIDER;
case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION:
return NOP_FALLBACK_SERVICE_PROVIDER;
case FAILED_INITIALIZATION:
throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG);
case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION:
// support re-entrant behavior.
// See also http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-97
return SUBST_PROVIDER;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
}
调用performInitialization函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
private final static void performInitialization() {
bind();
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) {
versionSanityCheck();
}
}
调用bind函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
private final static void bind() {
try {
List<SLF4JServiceProvider> providersList = findServiceProviders();
reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(providersList);
if (providersList != null && !providersList.isEmpty()) {
PROVIDER = providersList.get(0);
// SLF4JServiceProvider.initialize() is intended to be called here and nowhere else.
PROVIDER.initialize();
INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION;
reportActualBinding(providersList);
} else {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION;
Reporter.warn("No SLF4J providers were found.");
Reporter.warn("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation");
Reporter.warn("See " + NO_PROVIDERS_URL + " for further details.");
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
reportIgnoredStaticLoggerBinders(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
}
postBindCleanUp();
} catch (Exception e) {
failedBinding(e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e);
}
}
bind函数中已经见到了我们想寻找的警告信息。先分析一下其逻辑。整体上,通过findServiceProviders()函数去寻找Provider,放到ProviderList中。如果没找到,则输出我们寻找的错误信息。若找到则正常进行初始化,这个我们后续研究。继续探究找的过程和方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
static List<SLF4JServiceProvider> findServiceProviders() {
List<SLF4JServiceProvider> providerList = new ArrayList<>();
// retain behaviour similar to that of 1.7 series and earlier. More specifically, use the class loader that
// loaded the present class to search for services
final ClassLoader classLoaderOfLoggerFactory = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
SLF4JServiceProvider explicitProvider = loadExplicitlySpecified(classLoaderOfLoggerFactory);
if(explicitProvider != null) {
providerList.add(explicitProvider);
return providerList;
}
ServiceLoader<SLF4JServiceProvider> serviceLoader = getServiceLoader(classLoaderOfLoggerFactory);
Iterator<SLF4JServiceProvider> iterator = serviceLoader.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
safelyInstantiate(providerList, iterator);
}
return providerList;
}
这段代码发现了一个功能特性,就是在loadExplicitlySpecified函数中,你可以通过设置系统变量slf4j.provider,指定Provider实现类。
1
static final public String PROVIDER_PROPERTY_KEY = "slf4j.provider";
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
static SLF4JServiceProvider loadExplicitlySpecified(ClassLoader classLoader) {
String explicitlySpecified = System.getProperty(PROVIDER_PROPERTY_KEY);
if (null == explicitlySpecified || explicitlySpecified.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
try {
String message = String.format("Attempting to load provider \"%s\" specified via \"%s\" system property", explicitlySpecified, PROVIDER_PROPERTY_KEY);
Reporter.info(message);
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(explicitlySpecified);
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
Object provider = constructor.newInstance();
return (SLF4JServiceProvider) provider;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
String message = String.format("Failed to instantiate the specified SLF4JServiceProvider (%s)", explicitlySpecified);
Reporter.error(message, e);
return null;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
String message = String.format("Specified SLF4JServiceProvider (%s) does not implement SLF4JServiceProvider interface", explicitlySpecified);
Reporter.error(message, e);
return null;
}
}
若没配置(常见情况),则继续通过getServiceLoader寻找
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private static ServiceLoader<SLF4JServiceProvider> getServiceLoader(final ClassLoader classLoaderOfLoggerFactory) {
ServiceLoader<SLF4JServiceProvider> serviceLoader;
SecurityManager securityManager = System.getSecurityManager();
if(securityManager == null) {
serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(SLF4JServiceProvider.class, classLoaderOfLoggerFactory);
} else {
final PrivilegedAction<ServiceLoader<SLF4JServiceProvider>> action = () -> ServiceLoader.load(SLF4JServiceProvider.class, classLoaderOfLoggerFactory);
serviceLoader = AccessController.doPrivileged(action);
}
return serviceLoader;
}
getServiceLoader中通过Java中的java.util.ServiceLoader去寻找实现类
1
serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(SLF4JServiceProvider.class, classLoaderOfLoggerFactory);
java.util.ServiceLoader 是Java提供的一个用于服务发现的机制,它通过在类加载器范围内查找和加载给定接口或抽象类的实现类。ServiceLoader主要依赖于类加载器和 META-INF/services 目录下的服务提供者配置文件来实现服务的查找和加载。
当前情况下,classpath下自然找不到这些文件。providerList为空所以在bind函数中输出了之前我们关注警告信息。
下一篇我们再继续研究引入Logback框架的情况,估计你已经猜出大半了。